''rajinikanth pierre laval''
Name | Rajinikanth |
| Real Name | Shivaji Rao Gaikwad |
| Date of Birth | 12.12.1950 |
| Time of Birth | 11:54 P.M. |
| Place of Birth | Bangalore |
| Star/Rasi | Sirvana/Magaram |
| Color | Black |
| Height | 5 feet 9 inch |
| Weight | 70 Kg |
| Name of Spouse | Mrs. Latha Rajinikanth, Principal, |
| The Ashram | |
| Date of Marriage | 26.02.1981 4:30 A.M |
| Place of Marriage | Thirupathi |
| Date of Reception | 14.03.1981 6:00 A.M |
| Place of Reception | Taj Coromandal, Chennai |
| Names of Children | Aishwarya & Sowandarya |
| Address | 18, Raghava Veera Avenue, |
| Poes Garden, Chennai-86 | |
| Contact Phone | 2,499,129,124,990,270 |
| Fax | 24838890 (Raghavendra Mandapam) |
| Father's Name | Ramoji Rao |
| Mother's Name | Rambhai |
| Brother's Name | Sathya Narayana Rao & Nageshwara Rao |
| Guru | K.Balachandar |
| Spiritual Guru | Satchithananda Swamiji |
| Favourite God | Shri Raghavendra |
| Favourite Books | Books written by Shri Ramana Maharishi |
| Favourite City | Chennai |
| Favourite Colour | Black |
| Favourite Drinks | Juice & Curd |
| Favourite Foods | Chicken & Mutton items |
| Happiest Moments | To be alone |
| Worst Moments | Left the job of Conductor |
| Worst Period | 1978 - 1981 |
| Favourite Dress | White Kurtha |
| Favourite Place | Himalaya |
| Favourite Place in House | Pooja Room |
| Favourite Proverb | Beware of Everything -that is un true; stick to the Truth shall succeed slowly but steadily |
| Favourite work | Self-driving |
| Unforgettable Man | K.Balachandar |
| Unforgettable Function | Bassha Silver Jubilee Function |
| Unforgettable Friend | Sri Priya |
| First Film | Aboorva Ragangal |
| 50th Film | Tiger (Telugu) |
| 100th Film | Shri Raghavendrar |
| 125th Film | Rajathi Raja |
| 150th Film | Padyappa |
| Favourite Hollywood Actor | Sylvester Stallone |
| Favourite Indian Actor | Kamalhaasan |
| Favourite Actress | Rekha (Hindi) |
| Favourite Role | Romantic Roles |
| Most Valuable Item | Appreciation Letter from K.Balachander for the film "Mullum Malarum" |
| Favourite Language | English |
| Favourite Films | Hollywood Films |
| Favourite Novel | Kalki's Ponniyin Selvan & T. Janakiraman's Amma Vanthal |
| Favourite Cinema Scene | Duet Scene |
| Favourite Writer | Jayagandhan |
| Favourite Poet | Kannadasan |
| Favourite Musician | Illayaraja |
| Favourite Speaker | Vattal Nagaraj |
| Favourite Songs | Songs sung by Chandrababu |
| Favourite Film | Veera Kesari (Kannada) |
| Favourite Politician | Singapore President Lee Quan-u |
| Unforgettable Leader | Mahatma Gandhiji |
| About Mahatma Gandhiji | Form of Truth; Great Yogi |
| About Bharathiar | Real Rebel Poet |
| About Kamarajar | Real "Padikatha Methai" |
| About Periyar | Real Spiritualist |
| About Annadurai | Great Leader |
| About Kalaigar | The only leader for Tamil Community |
| About M.G.R | Guardian to Tamil Cinema |
| About Shjivaji Ganeshan | Dictionary of Tamil Cinema |
| About Jayshankar | Sportiveness |
| About Shivakumar | Punctuality |
| About Kamalahaasan | Sincerity |
| Message to Fan | Live & Let Live |
| About Rajinikanth | I live for myself ; I don't care anybody but I respect everybody |

 Governments do not issue patents just for an idea.Ideas, thoughts or inspirations do not not qualify for a patent.
Governments do not issue patents just for an idea.Ideas, thoughts or inspirations do not not qualify for a patent.



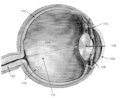 As our population ages, impaired vision caused by damaged retinas has increased.
As our population ages, impaired vision caused by damaged retinas has increased. Researchers at MIT have created the world's first batteries constructed from microscopic viruses.
Researchers at MIT have created the world's first batteries constructed from microscopic viruses. Elizabeth Redmond of Chicago is using the law of thermodynamics to create floor tiles that compress to generate and distribute electricity.
Elizabeth Redmond of Chicago is using the law of thermodynamics to create floor tiles that compress to generate and distribute electricity. Shoushan Fan, Kaili Jiang and Lin Xiao, scientists at Tsinghua University in Beijing, have invented a super-thin loudspeaker (one thousandth the width of a human hair).
Shoushan Fan, Kaili Jiang and Lin Xiao, scientists at Tsinghua University in Beijing, have invented a super-thin loudspeaker (one thousandth the width of a human hair). Anil Sethi, chief executive of the Swiss company Flison, holds a dark polymer foil. A paper-thin foil 200 times lighter than glass solar material. So light, it can be stuck to the sides of a building. So light, it can be mass-produced in rolls like packaging material.
Anil Sethi, chief executive of the Swiss company Flison, holds a dark polymer foil. A paper-thin foil 200 times lighter than glass solar material. So light, it can be stuck to the sides of a building. So light, it can be mass-produced in rolls like packaging material.
 This is one of those cool inventions that provides peace of mind for securing your information.
This is one of those cool inventions that provides peace of mind for securing your information. Most ciphers will use passwords that are four to eight characters in length, but a 128-bit AES cipher uses a 16 character password which is extremely difficult to hack.
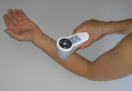
Most ciphers will use passwords that are four to eight characters in length, but a 128-bit AES cipher uses a 16 character password which is extremely difficult to hack. Biometric authentication is a technology that recognizes physical or behavioral characteristics such as fingerprints, palm geometry, retina patterns, voice and signature. Fingerprint recognition is the most popular because it's easier to use.
Biometric authentication is a technology that recognizes physical or behavioral characteristics such as fingerprints, palm geometry, retina patterns, voice and signature. Fingerprint recognition is the most popular because it's easier to use. The Zoombak is one of those cool inventions utilizing gps technology.
The Zoombak is one of those cool inventions utilizing gps technology. This is one of those green inventions that captures energy.
This is one of those green inventions that captures energy. The tragic loss of lives from the lack of safe drinking water in the aftermath of the tsunami in Indonesia and the hurricane in Louisana, motivated inventor Micheal Pritchard to find a solution.
The tragic loss of lives from the lack of safe drinking water in the aftermath of the tsunami in Indonesia and the hurricane in Louisana, motivated inventor Micheal Pritchard to find a solution. Sawa Hiroshi is an engineer employed by the Oriental Development Company in Japan.
Sawa Hiroshi is an engineer employed by the Oriental Development Company in Japan. It takes about 30 minutes to make a roll and each one is made with the equivalent of 40 sheets of standard size office paper.
It takes about 30 minutes to make a roll and each one is made with the equivalent of 40 sheets of standard size office paper. The Powermat is a wireless charger for hi tech gadgets. You simply place your gadget on the mat to charge it.
The Powermat is a wireless charger for hi tech gadgets. You simply place your gadget on the mat to charge it. If you drink alcohol don't operate a vehicle. But the reality is that people rely on their own sense of sobriety if they have a glass of wine at a restaurant or a couple of beers during a sporting event.
If you drink alcohol don't operate a vehicle. But the reality is that people rely on their own sense of sobriety if they have a glass of wine at a restaurant or a couple of beers during a sporting event. If there is one thing that consumers have in common when it comes to their hi tech gadgets - it's their concern about cracked and scratched screens.
If there is one thing that consumers have in common when it comes to their hi tech gadgets - it's their concern about cracked and scratched screens. Oganovo is a company based in San Diego, California.
Oganovo is a company based in San Diego, California. A nanobot particle made from glass is being developed that can absorb pollutants from contaminated water.
A nanobot particle made from glass is being developed that can absorb pollutants from contaminated water. Physicist and inventor, Bruno Berge, has created a liquid optical lens.
Physicist and inventor, Bruno Berge, has created a liquid optical lens. Chungpin Liao, a professor at the Graduate School of Electro-Optic and Material Science of National Formosa University in Taiwan has invented an organic battery that creates electricity when wet.
Chungpin Liao, a professor at the Graduate School of Electro-Optic and Material Science of National Formosa University in Taiwan has invented an organic battery that creates electricity when wet.

 This future invention is a device for delivering medication and vaccinations through the skin.
This future invention is a device for delivering medication and vaccinations through the skin. Scientists at Standford University are developing future inventions using e-Texiles.
Scientists at Standford University are developing future inventions using e-Texiles.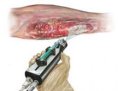 One of the
One of the  Among the future inventions in e-readers is this paper thin, flexible film that reads like a magazine or newspaper.
Among the future inventions in e-readers is this paper thin, flexible film that reads like a magazine or newspaper.